Understanding Brain Tumours: Types, Symptoms and Treatment Options
Brain tumours are a complex and often challenging condition that can significantly impact an individual's health and well-being. Understanding the different types of brain tumours, recognizing their symptoms, and exploring available treatment options are crucial in effectively managing this condition.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of brain tumours, shedding light on their various types, common symptoms, and the range of treatment options available.
Types of Brain tumours:
Brain tumours are classified into two main categories: primary and secondary. Primary brain tumours originate within the brain tissue, while secondary brain tumours, also known as metastatic tumours, result from cancer cells that have spread from other body parts. Common types of primary brain tumours include gliomas (such as astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas), meningiomas, and medulloblastomas. Each type of tumor has distinct characteristics and requires tailored treatment approaches.
Symptoms and Warning Signs:
The symptoms of tumor in brain can vary depending on its size, location, and growth rate. Some common warning signs include persistent headaches, seizures, and changes in vision or hearing, difficulty with balance or coordination, cognitive and memory problems, and personality changes. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and unexplained weight loss. It is important to note that these symptoms can also indicate other conditions and a proper medical evaluation is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic Procedures:
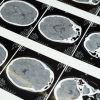
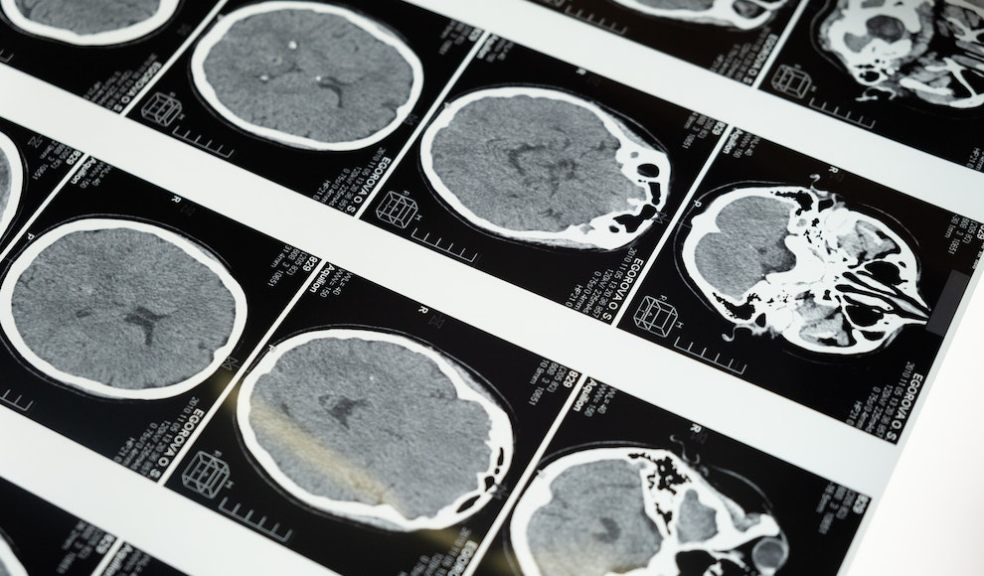
Diagnosing a brain tumor involves a series of diagnostic procedures to determine the cancer's type, location, and extent. These procedures may include imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) scans, and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to obtain a tumor tissue sample for further analysis. These diagnostic procedures provide critical information to guide the treatment plan.
Treatment Options:
The treatment of brain tumours depends on various factors, including the type, size, and location of the cancer, as well as the individual's overall health. The primary treatment modalities for brain tumours include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Surgery aims to remove as much of the cancer as possible while preserving healthy brain tissue. Radiation therapy utilizes high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells, while chemotherapy uses drugs to kill or inhibit their growth.
Advances in Targeted Therapies:
In recent years, significant advancements have been made in developing targeted therapies for brain tumours. Targeted therapies involve drugs or other substances targeting certain molecules or genetic mutations in cancer cells, disrupting their growth and survival. These therapies offer a more precise and personalized approach, improving treatment outcomes and minimizing side effects.
Supportive Care and Rehabilitation:
Managing the effects of brain tumours extends beyond medical treatments. Supportive care is crucial in enhancing the quality of life for individuals with brain tumours. This may include pain management, psychological support, rehabilitation services, and assistance with managing treatment side effects. Supportive care addresses the physical, emotional, and social aspects of the individual's well-being throughout their journey.
Conclusion:
Understanding the intricacies of brain tumours, including their types, symptoms, and available treatment options, is vital in effectively managing this complex condition. Early detection, accurate diagnosis, and a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the individual's needs are essential for the best possible outcomes. Ongoing research and advancements in targeted therapies hold promise for further improving treatment strategies and ultimately enhancing the prognosis and quality of life for individuals affected by brain tumours.