PRP for Thinning Hair: A Complete Guide to How It Works, Who It Helps, and What Results to Expect
Hair thinning and hair loss are challenges that affect millions of people worldwide, impacting self-confidence and overall well-being. Among the various treatments available, PRP for thinning hair has emerged as a scientifically supported, minimally invasive solution that harnesses the body’s natural healing mechanisms to stimulate hair growth.
This comprehensive guide explains how PRP works, identifies who is most likely to benefit, and sets realistic expectations for results.
Understanding PRP Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy involves using a patient’s own blood to promote tissue regeneration and stimulate growth. Platelets are rich in growth factors, proteins that facilitate healing and cellular regeneration. When these growth factors are injected into the scalp, they can help reactivate dormant hair follicles, enhance blood supply, and encourage the production of thicker, healthier hair.
PRP therapy has a long-standing history of use in medical disciplines such as orthopedics, dermatology, and cosmetic medicine. Its application in hair restoration builds on this foundation, leveraging the body’s intrinsic regenerative and healing mechanisms to stimulate dormant hair follicles, enhance scalp health, and promote natural hair growth.
The Science Behind PRP for Hair Loss
PRP works by leveraging the regenerative properties of platelets. Hair growth occurs in cycles, anagen (growth phase), catagen (transition), and telogen (resting). Thinning hair often results from follicles prematurely entering the telogen phase. Growth factors in PRP, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), encourage follicles to remain in or re-enter the anagen phase, promoting thicker and more robust hair.
The PRP treatment process typically involves four main steps:
- Blood Collection – A small sample of the patient’s blood is drawn.
- Centrifugation – The blood is spun in a centrifuge to separate platelet-rich plasma from other components.
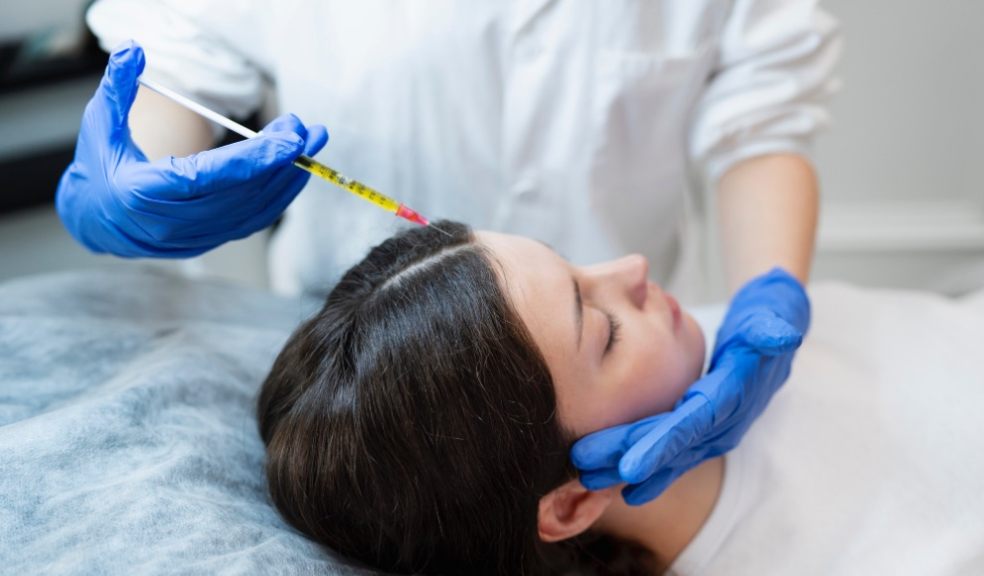
- Scalp Injection – The PRP is carefully injected into thinning areas of the scalp.
- Follicle Stimulation – Growth factors interact with hair follicles, enhancing cellular activity and improving hair density over time.
This method is non-surgical and minimally invasive, harnessing the patient’s own biological mechanisms to stimulate hair growth, making it a safe and low-risk treatment when administered by a qualified medical professional.
Who is an Ideal Candidate for PRP?
PRP therapy is most effective for individuals with active hair follicles who are experiencing thinning or early-stage hair loss. Key considerations include:
- Pattern Hair Loss – Both male and female pattern baldness respond well to PRP.
- Thinning Hair, Not Complete Baldness – PRP relies on existing follicles to stimulate growth; it is less effective in areas with complete follicular loss.
- Healthy Scalp and Hair Follicles – Conditions such as scalp scarring may limit PRP effectiveness.
- Preference for Non-Surgical Treatment – Those seeking alternatives to hair transplant surgery can benefit from PRP as a stand-alone therapy or adjunct.
Combining PRP with other hair restoration modalities can enhance outcomes in select cases.
Treatment Process and Session Frequency
PRP therapy is typically performed in a series of sessions. A common regimen includes:
- Initial Phase: Monthly treatments for the first three to four months to stimulate follicular activity.
- Maintenance Phase: Follow-up sessions every three to six months to sustain hair density and prevent regression.
During each session, a trained provider draws blood, processes it, and performs precise scalp injections. While the procedure is generally well-tolerated, minor side effects such as scalp tenderness, mild swelling, or temporary redness may occur. Serious complications are rare when performed by qualified professionals, and strict adherence to sterile techniques ensures safety.
For professional training on PRP injection techniques and patient safety, consult Injector Training.
Expected Results and Timelines
Results from PRP therapy vary depending on age, genetics, and the severity of hair thinning. Typical progress includes:
- 1 Month: Mild scalp sensitivity and initial reduction in shedding.
- 2–3 Months: Early signs of hair regrowth may appear; hair strands may feel thicker and stronger.
- 4–6 Months: Noticeable improvement in hair density and thickness.
- 6–12 Months: Optimal results are often achieved, with sustained improvement in hair volume.
It’s important to note that PRP is not a one-time solution. Ongoing maintenance treatments are often necessary to sustain results and ensure long-term improvement in hair density and quality.
Safety Considerations
PRP therapy is generally safe due to its autologous nature, using the patient’s own blood minimizes risks of allergic reactions or disease transmission. Common side effects are usually mild and transient:
- Temporary scalp tenderness or swelling
- Minor bruising at injection sites
- Mild redness or itching
Selecting a qualified provider is essential. Board-certified dermatologists or licensed medical professionals trained in PRP procedures ensure proper technique, maximizing efficacy while minimizing risk.
Choosing a Reputable PRP Provider
When selecting a clinic or provider, consider:
- Medical Credentials: Ensure practitioners are board-certified and trained in aesthetic medicine or dermatology.
- Experience and Track Record: Clinics with a history of successful PRP treatments demonstrate reliability.
-
Customized Treatment Plans: Individualized protocols based on hair density, scalp condition, and patient goals improve outcomes.
Patient Testimonials: Real-world feedback offers insight into the quality of care and results. - Technology and Equipment: High-quality centrifuges and injection tools are critical for effective PRP preparation and delivery.
A reputable provider will offer a clear treatment plan, set realistic expectations, and provide post-treatment guidance.
Combining PRP with Other Hair Restoration Treatments
PRP can complement other therapies to enhance hair regrowth and density:
- Topical Solutions (e.g., Minoxidil): Supports ongoing follicle stimulation.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Improves scalp circulation and follicle health.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: PRP may improve graft survival and accelerate post-operative healing.
Combining therapies should always be guided by a qualified medical professional to maximize results while ensuring patient safety.
Conclusion
PRP for thinning hair is a clinically supported, minimally invasive treatment that leverages the body’s natural growth factors to stimulate hair follicles, improve density, and enhance hair quality. While results vary based on individual factors, many patients experience noticeable improvements within months, especially when treatments are performed by experienced professionals and maintained appropriately.
For those exploring non-surgical options for hair restoration, PRP offers a compelling, science-backed alternative. Choosing a reputable clinic and following a structured treatment plan are critical steps toward achieving the best outcomes.